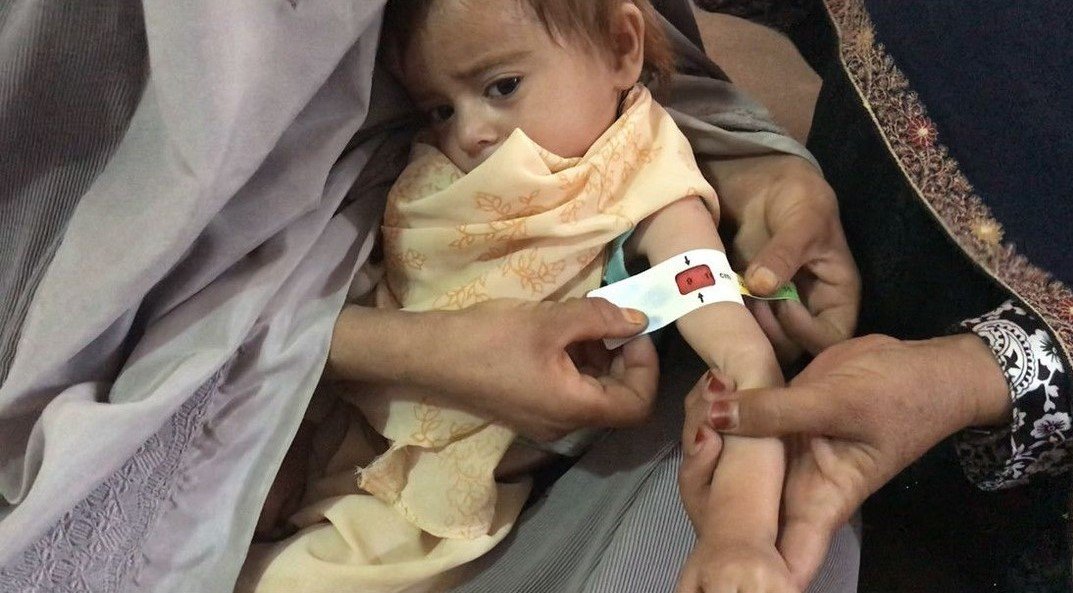
Balanced nutrition at the right time is necessary for the survival, health, and development of children. Well-nourished children respond well in fighting diseases and other crises, hence also much more prepared to grow and learn and act like productive members of society. In contrast, poor nutrition impacts education, health, and well-being through generation.
The situation is quite dire in Pakistan, with underweight, stunting, and wasting heavenly prevalent in the country, and the picture of child malnutrition in Gilgit-Baltistan is also gloomy with two in ten children under the age of five stunted, moderately or severely, six percent severely underweight, and forty-six percent moderately wasted, or too thin as reported by the Multiple Cluster Survey (MICS), 2017.
The following factors: wretched poverty, high illiteracy, harsh weather, floods, and unchecked population growth are most responsible for children’s malnutrition in Gilgit-Baltistan that will be put each part of it under the magnifying glass in the subsequent paragraphs.
Poverty is the most prominent factor in explaining malnutrition. Although begging culture doesn’t exist in Gilgit-Baltistan society, yet poverty is chronic and pervasive. Multidimensional poverty index puts poverty number at 45 percent in Gilgit-Baltistan, which is equal to Sindh, lower than KPK, and higher than Punjab and AJK. In Gilgit-Baltistan, 62 percent of the children living in the poorest households are stunted, whereas 31 percent of underweight children living in the poorest households also witnessed higher prevalence compared to 26 percent and 7 percent of children in the richest households that are stunted and underweight, according to the report of Multi-Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS).
Moreover, education level also correlates with nutritional status meaning that educated family has higher living standard and good information on a healthy basket of goods than those who have little education or no education. For example, the MICS report states that among women with higher education, 25 are stunted, 8 percent underweight, and 1 percent are stunted compared to more than 54 percent for stunting and 25 percent underweight among children whose mothers are pre-school or have no schooling. By comparing the literacy rate with each region of malnutrition indicators among children, we found that Diamer, with the lowest rank in literacy rate, has the highest rate of underweight and stunting; while Gilgit and Hunza, with the highest literacy rate, has the lowest rate of stunting.
Harsh weather, which is unfavorable for agriculture, is another bottleneck for the availability of food among children, pronouncing a high risk of food insecurity in the region. Due to prolonged winter, the local farmers cultivate one crop in all districts except Gilgit, where the temperature remains high. With outdated technology used by farmers, the output remains discouraging. Even though the wheat subsidy is available and affordable, yet the whole region for vegetables and other staple food is dependent on the other provinces in the off-season. Transport costs, with far distance to Punjab, burden the locals with inflation. Additionally, on account of the poor canal system, a large part of the land is barren. Precisely, weather and geographical position account for food unavailability in the region that triggers child malnutrition.
Moreover, every year floods hit at least any part of the region and make the life of people miserable with losing crops, suffering infrastructure damages, and worsening financial conditions. After the math of disaster, malnutrition may be more pronounced with the shortage of water, food, and poor living conditions. Children being affected have little immunity to diseases like diarrhea, acute respiratory infections, and tuberculous. Areas such as Ghizer, Ghanche, and Khapulo being more prone to floods have a high rate of child malnutrition as compared to less prone areas.
Additionally, large family size also results in food insecurity, for it decreases per capita food availability in family. Globally, Pakistan’s status in infertility rate is next to second with 3.2 percent on average, which is despicable where 40 percent population are already facing food insecurity. Hence, the government is finding it difficult to create income-generating activities to match the growing need while meeting the backlog.
Dealing with malnutrition requires a pragmatic approach that systematically brings vulnerable families out of troubled water. Like, China systematically lifted 100 million people out of extreme poverty through skills empowerment. Merely giving cash transfers doesn’t work. Take an example of Pakistan’s successive social safety programs: currently the Ehsaas program and former the BISP; yet poverty is continuing to spiral upward.
The government of Gilgit-Baltistan is dependent on the financial resources of the federal government. However, the federal government on account of fiscal constraints cannot evaluate poverty of all. As It barely finances its current expenditures and depends on loans for development projects resultantly debt crossing 100 percent of GDP. Moreover, 40 percent of the country’s budget is spent on debt servicing and 16 percent on defense expenditures. At last, a small portion of the pie is left for solving people’s concerns.
On the back of the myriad of problems, it is also the responsibility of citizens to work collectively with the government. We, for that, must contribute to public work and scarify our resources to establish training centers and workshops that empower unemployed youths and women in market oriented skills to increase their productivity. Then automatically it will translate into the standard of living that is the sine qua non for food affordability.
In a nutshell, child malnutrition is a pressings issue that is needed to do away with far-reaching structural reforms that systematically solve people’s problems elevating their social status. Wretched poverty, high illiteracy, harsh weather, and uncontrolled population growth accounted for poor nutrition intake. On account of pervasive malnutrition in the country, food insecurity has emerged as a new and the biggest challenge for national security.




 Arts, Culture & Heritage2 years ago
Arts, Culture & Heritage2 years ago
 KIU Corner2 years ago
KIU Corner2 years ago
 Arts, Culture & Heritage2 years ago
Arts, Culture & Heritage2 years ago
 KIU Corner2 years ago
KIU Corner2 years ago
 Arts, Culture & Heritage2 years ago
Arts, Culture & Heritage2 years ago
 Tourism2 years ago
Tourism2 years ago
 Opinion3 years ago
Opinion3 years ago
 Current Affairs2 years ago
Current Affairs2 years ago

































